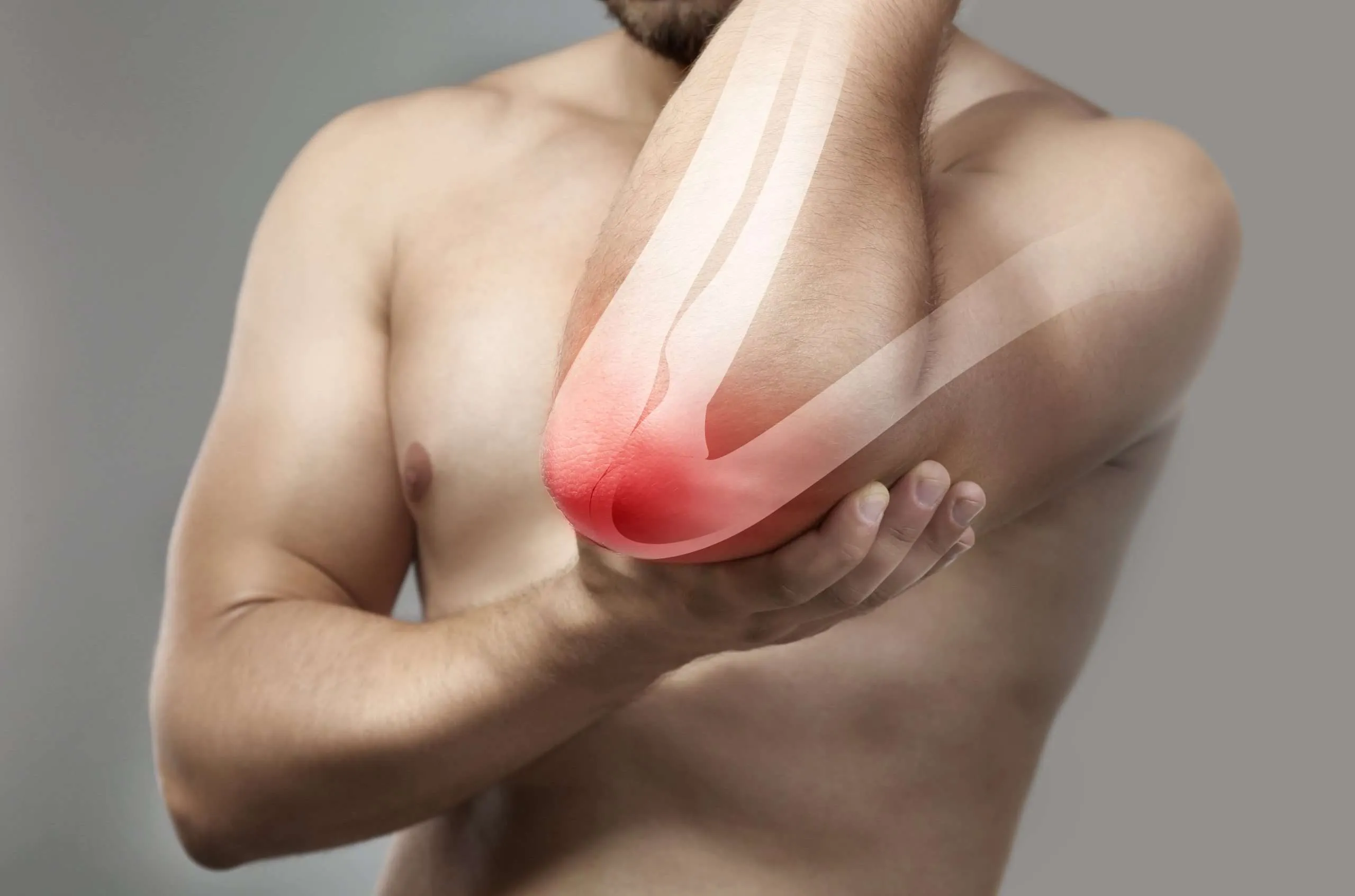
Elbow joint pain refers to discomfort, stiffness, or aching in or around the elbow. It can affect people of all ages and may result from injuries, overuse, or underlying medical conditions. Proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment.
This condition occurs from overuse of the forearm muscles, causing inflammation in the tendons outside the elbow. It's common in athletes and people with repetitive arm movements.
Golfer's elbow causes pain on the inner side of the elbow due to overuse of wrist flexor muscles. It often affects golfers, tennis players, and people lifting heavy objects.
Inflammation of the bursa (a fluid-filled sac) at the back of the elbow can cause swelling and pain. Repeated pressure or trauma is a common cause.
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint inflammation, stiffness, and pain in the elbow. These conditions may worsen over time without treatment.
Falls or direct impacts can lead to fractures or dislocations, causing severe pain, swelling, and loss of movement in the elbow joint.
Resting the joint and applying ice packs can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
A physical therapist can design exercises to strengthen the muscles around the elbow and improve flexibility.
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescription medications can manage pain and inflammation.
Using an elbow brace can support the joint and limit movement, aiding in recovery.
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues or joints.
If elbow pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by severe swelling, numbness, or loss of movement, seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can prevent long-term complications.
Subscribe to read the full article.
Subscribe Now